Solar Power System—Your Friendly Guide to Going Solar
If you’re thinking of switching to clean energy, you’ve probably Googled something like “solar power system” and found yourself staring at some technical articles or general overviews. This guide breaks down what a solar power system is, how it works, why it’s a smart investment—and all the practical stuff you need to decide and act. This guide is friendly, informal, and filled with practical advice.
What is a Solar Power System?
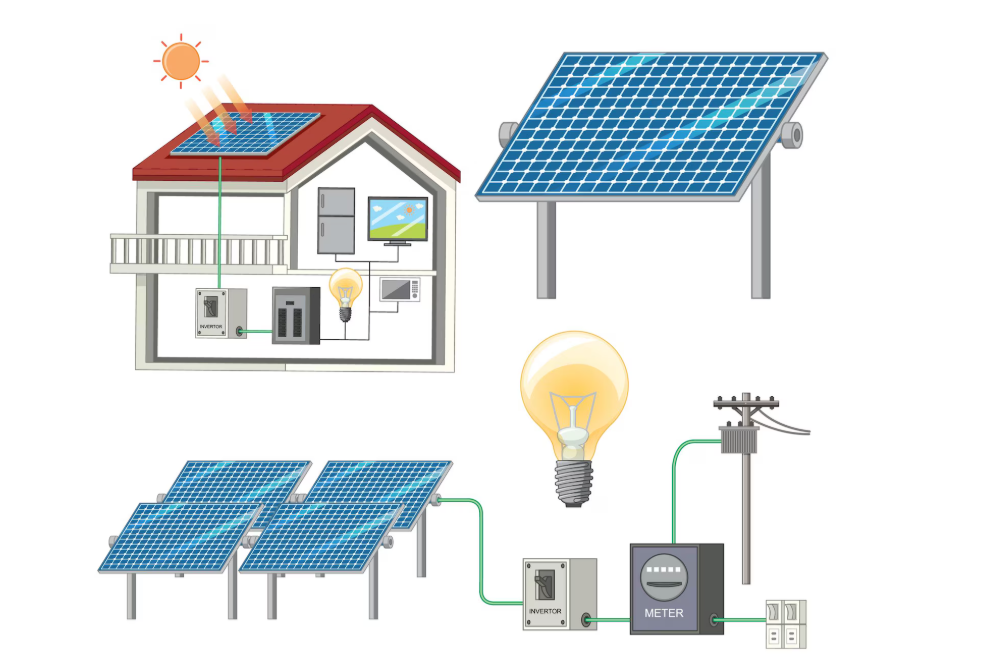
A solar power system (also called a solar energy system) is basically a setup that takes sunlight and turns it into usable electricity for your home, business, or industrial facility. It typically involves photovoltaic (PV) panels, mounting structures, inverters, wiring, and sometimes batteries or grid connection.
In simple terms: Sunlight → PV panels → DC electricity → inverter → AC electricity → your appliances.
Why this matters: With rising electricity costs, grid instability, and climate goals, installing a solar power system has gone from niche to mainstream.
Why You Should Consider One
- Lower utility bills: Once installed, you generate your own electricity and reduce reliance on the grid.
- Clean energy: Solar emits no direct greenhouse gases, helping reduce your carbon footprint.
- Energy independence: Whether it’s a home or business, you gain more control over energy supply.
- Increased property value: Systems frequently add value to homes or buildings.
- Government incentives: Especially in India, there are subsidies, net metering, and favorable policies.
Key Components of a Solar Power System
- Photovoltaic (PV) panels—these are what capture sunlight. When choosing panels, you’ll look at efficiency, brand, warranty, and cost.
- Inverter—Converts DC electricity (from the panels) into AC electricity (used by your home).
- Mounting & Wiring refers to the racking system that secures the panels and the cabling that connects them all.
- Meter and Grid Connection/Battery Storage: If you stay connected to the grid, you may get credited for excess electricity. If you go off-grid or want backup, battery storage is added.
- Installation & Monitoring—The physical installation, plus software/hardware to monitor performance, maintenance, cleaning, etc.
How Much Does It Cost? (And What Affects the Price)
In India especially, one of the first questions is, “What’s the solar system price?” The answer: it depends. Factors include system size (kW), panel brand, installation complexity (roof type, angle, shading), battery inclusion, and regulatory incentives.
- On-grid rooftop systems without batteries tend to cost less.
- Add batteries, an off-grid setup, or high-end panels → cost goes up.
- Your site conditions matter (roof strength, orientation, shade, etc.).
- Government subsidy or net-metering policy can significantly impact payback.
As a rough ballpark: for a typical home (say 3–5 kW), you might spend anywhere from ~₹1 to ₹2 lakh (depending on quality and region). But check local quotes before committing.
Choosing the Right Equipment & Manufacturer
When you’re comparing, keep these in mind:
- Go with trusted solar panel manufacturers. In India for instance, brands like Delta Power are known for module manufacturing capacity and quality.
- Panel efficiency and warranty matter (25 years+ is common for panels).
- For the inverter, look for strong tech support and warranty.
- Installation partner (EPC or installer) matters a lot—quality of work influences long-term performance.
- Ask for monitoring, maintenance, and clear terms.
- If you’re looking at the price of a solar panel for a home in India, you’ll want to factor in post-installation performance and savings, not just upfront costs.
Step-by-Step: How to Install a Solar Power System
- Site Survey & Load Analysis – Check the roof size, orientation, and shading, and estimate your electricity use.
- Design & Equipment Selection—Choose the system size, panel and inverter brands, mounting, etc.
- Permits & Grid Connection—If you are connecting to the grid or want net metering, there are approvals to handle.
- Installation & Commissioning—Racks are mounted, panels fixed, wiring done, inverter connected, and system commissioned.
- Monitoring & Maintenance—Panels need minimal maintenance (cleaning, checking for faults). Monitoring helps detect issues early.
- Savings & ROI Review: After a few months, review your actual performance vs. expected and track your payback period.
On-Grid vs Off-Grid Systems
- On-grid systems: Connected to the utility grid. You can draw from the grid when solar production is low and feed excess back. Lower battery cost.
- Off-grid systems: No grid connection. Requires battery storage and perhaps a backup generator. Off-grid systems are more expensive, but they offer complete independence.
- Choose based on location, grid reliability, budget, and goals.
Major Trends & Technologies in Solar
- Bifacial modules and high-efficiency mono-PERC/N-type panels: More output per area, higher cost but better ROI.
- Battery storage & integration: As batteries become cheaper, more homeowners go for systems with storage.
- Smart monitoring and IoT: Track your system’s performance in real time.
- Drone aerial photography can be used for site surveys—drones help inspect roofs, shading, and panel cleanliness more efficiently.
- Manufacturers are scaling up: In India and globally, manufacturing capacity is expanding. For example, Delta Power has grown capacity to 4.5 GW.
What to Ask Before Signing a Contract
- What is the solar system price, including installation, mounting, wiring, and permits?
- Which solar panel manufacturers are you partnering with; what are the brand, model, efficiency, and warranty?
- Will you provide a performance guarantee (kWh/year)?
- Who handles monitoring and maintenance?
- What’s the estimated payback period and projected savings?
- Is net metering included/handled?
- What happens in case of roof damage or panel fault?
- If you include battery storage, what battery type, warranty, and expected lifetime?
- Are there bonus features like drone aerial photography or remote monitoring?
- Are incentives or subsidies applied and clear in the quote?
Real-Life Example: Home Solar in India
Let’s imagine you live in Panchkula, Haryana (same city as me!). You use ~300 units (kWh) per month. A 5 kW rooftop solar power system might generate ~20–22 kWh/day depending on sunlight, shading, and orientation; that’s ~600–660 kWh/month. With excellent net metering, you might offset most of your usage. Suppose your system costs ₹1.8 lakh, your annual savings are ₹1.0-1.2 lakh (depending on tariff), and your payback is ~1.5-2 years—after that, it’s effectively “free” power (barring maintenance).
Benefits & Limitations—Be Realistic
Benefits
- Predictable cost (after installation).
- The system provides clean, renewable energy.
- This approach lessens reliance on escalating grid tariffs.
Limitations
- High upfront cost.
- Roof must be suitable (orientation, shading, strength).
- Battery systems still add significant cost.
- Performance depends on local solar radiation, maintenance, and panel cleanliness.
- If you move house, ownership or transfer of the system can get tricky.
How to Maximise Your ROI
- Use the system output smartly—for washing, AC or high-load tasks at midday when solar is producing.
- Keep panels clean—dust and bird droppings reduce output.
- Monitor performance monthly—if output drops unexpectedly, investigate.
- Use efficient appliances so you don’t oversize your system unnecessarily.
- Look for subsidies and net-metering rules in your state.
- Consider future-proofing: maybe start with a basic system today and expand later with storage or more panels.
Frequently Asked Questions (10 People Also Ask / FAQs)
What size solar power system do I need for my home?
– It depends on your monthly electricity consumption (kWh), roof space, and budget. For example, a home using 300 units/month might aim for a 4-6 kW system.How much does a solar power system cost in India?
– Costs vary widely depending on size, brand, battery inclusion, site conditions, and region. A rough benchmark: ~₹30,000–₹40,000 per kW for on-grid rooftop (as of 2025).What is the payback period for a home solar system?
– With favorable net metering and subsidies, payback in many Indian homes can be 3-5 years, sometimes less in high-tariff areas.Which solar panel manufacturers are the best?
– Look for established, Tier-1 manufacturers with excellent warranty, efficiency, and service. For example, one established manufacturer in North India is Delta Power.Do I need a battery with my solar power system?
– You do not necessarily need a battery if you are connected to the grid and using net metering. Battery makes sense if you want backup or live off-grid.What happens if I move home after installation?
– You’ll need to verify contract terms: whether the system can be transferred to the new owner or removed. You should also check if the installation requires you to enter into a lease agreement.How much maintenance is required?
– Very little. Panels may need cleaning once in a while; check inverter status and monitor output. No moving parts (for standard PV) means low maintenance.How does shading affect system performance?
– Quite significantly. Even small, shaded parts of your roof can reduce output by 10–30% or more. Proper site survey is essential.Can I get government subsidies for a solar power system in India?
– Yes—many states and central government schemes offer subsidies, low-interest loans, or favorable net metering. Check your local energy department.Are solar panels suitable for all roofs?
– Most roofs can work, but you’ll need sufficient space, favorable orientation (south-facing in India), minimal shading, and structural strength. Flat roofs often need extra mounting.
Final Thoughts
Investing in a solar power system is no longer futuristic—it’s practical, economic, and environmentally smart. With the right planning—choosing reputable solar panel manufacturers and accounting for solar system price, installation quality, site conditions, maintenance, and monitoring—you can enjoy lower bills, clean energy, and peace of mind.
If you’re ready to ask for quotes, start by analyzing your electricity usage, roof space, and budget. Then reach out to credible installation partners with clear breakdowns: equipment cost, installation, warranty, and service plan. Don’t simply pick the cheapest—value, brand reliability, and after-sales service matter if you want your system to last 20-25 years.
Let the sun do the heavy lifting. Your home, pocket, and the planet will thank you.
