Air Quality Monitoring Systems
Air in our atmosphere is a mixture of several invisible and odourless gasses. It consists of 78% nitrogen, about 21% Oxygen and less than 1% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide and small amounts of other gasses as well as the varying amount of water vapour. Even though there is no regular air pollution monitoring systems, we do feel and know that the quality of the air we breathe is declining because of the introduction of particulates and harmful substances into the Earth’s atmosphere. It causes diseases, allergies, death to humans, damages to other living organisms such as food crops and animals and the natural or built environment. The quality of air depends upon the amount of pollutant present in the air.
Air Quality Monitoring Devices
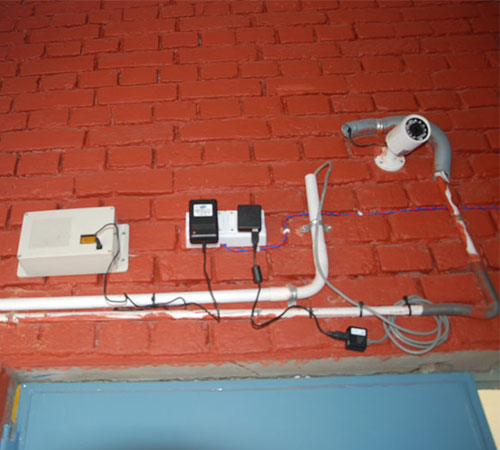
An Air Quality Monitoring device can help in analysing and keeping track of the amount of pollutants.

Air Quality Monitoring System

Real Time Air Quality Monitoring System

Air Quality Monitoring

Air Monitoring
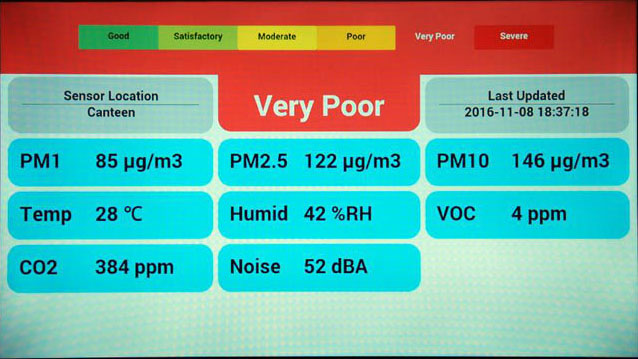
Air Quality Monitoring System
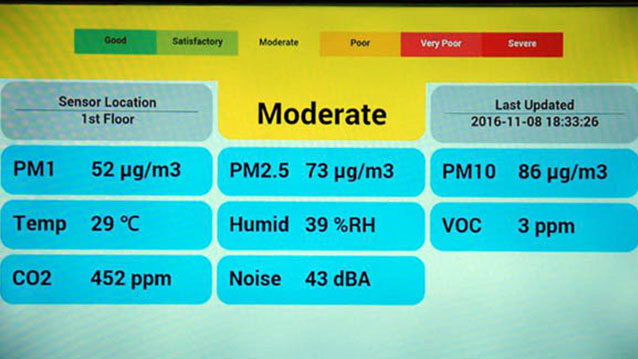
Air Quality Monitoring

Real Time Air Quality Monitoring System
What is air pollution monitoring system?
The term indicates the state of the air around us.
- Good AQ refers to the clean, unpolluted and clear air. Clean air is essential to maintain the balance of all kinds of life on the planet.
- Poor AQ occurs when pollutants/emissions reach a high enough concentration to affect health and the environment. It is caused because of
natural reasons such as volcanic - The eruption, windstorm dust
- human-made reasons such as volcanic eruption, windstorm dust

There are two types of Air Quality that one has to look out for
Outdoor Air Quality
Outdoor AQ can be described as the quality of outdoor air present in the surrounding environment. The air pollution monitoring system would be useful in measuring the level of air pollutants. Air pollutants can be in any form – gas, liquid or solid substance that has been emitted into the atmosphere and in high enough concentrations causing a harmful impact in the wider area.
- The pollutants emitted directly into the air are called ‘primary pollutants.
- The ‘secondary pollutants’ are formed in the air when they react with other pollutants.
Emissions can be any substance released into the air from natural or human sources –
- The flow of gasses
- Liquid droplets
- Solid particles
All emissions do not become air pollutants, but many do cause significant health and environment problems.
Some air pollutants in an area depends on
- The number and size of emission sources
- The topography
- Weather
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Outdoor IAQ refers to the quality of air – inside and around the buildings and structures, mainly as it relates to the comfort and health of building occupants.
Recognizing and controlling common indoor elements can help reduce the risk of indoor health concerns. Health effects caused by indoor air elements may be experienced soon after exposure or, possibly, years later.
Elements affecting Air Quality
Carbon Di Oxide (CO2)
- A natural component of air
- Emitted by humans
- Related to human metabolic activity
- Indoor concentrations elevated as compared to outdoor
- High level of CO2 result in drowsiness, headaches, or lower function activity levels
Carbon Mono-Oxide (CO)
- one of the most acutely toxic air contaminants
- colorless, odorless and tasteless gas slightly less dense than air
- reduces oxygen capacity of the blood cells
- low and moderate concentrations can cause fatigue, angina, reduced vision and effect on the nervous system
- high levels can lead to nausea, unconsciousness and even death
Particulate matter
- liquid matter or microscopic solid suspended in the Earth’s atmosphere
- exposure can cause
- short-term health effects such as throat, eye, nose and lung irritation, coughing, sneezing, runny nose and shortness of breath
- long-term health effects such as asthma, lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, respiratory diseases, premature delivery, birth defects, and premature death
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC)
- compounds released as gasses from certain solids or liquids
- emitted by products such as paints & lacquers, cleaning fluids, pesticides, building materials & furnishing, copiers, printers, coated paper, glues, adhesives, permanent markers, photographic solutions, etc.
- health effects of VOC are: eye nose and throat irritation, difficulty in breathing and nausea
Some other elements are:
- Cigarette smoke
- Mould
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Formaldehyde
- Radon gas
- Ozone
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Fine and Coarse Particles
- Lead
- Sulphur Dioxide
Long Term Effects
- heart disease, cancer, and respiratory diseases such as emphysema, asthma, bronchitis can be severely debilitating or fatal
- Damage to people’s nerves, kidneys, brain, liver, and other organs
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic bronchitis
- Accelerated aging of the lungs
- Loss of lung capacity
Taking Solar PV further with BIPV?
Immediate Effects
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, headaches, dizziness, and fatigue, nausea, wheezing, chest pain
- Diseases like asthma, sinusitis, etc.
- Colds or other viral diseases
- Aggravated respiratory and cardiovascular illness
- Added stress to lungs and heart, which must work harder to supply the body with oxygen
- Damaged cells in the respiratory system
- Reduced resistance to infection
- Increased fatigue
- Weakened athletic performance
- irregular heartbeat
What is an Air Quality Monitoring device?
Air Quality Monitoring device is a system set up to:
- Analyze the quality of outdoor as well as indoor air
- track down any pollutants that are present in the air
It is comprised of sensors which collects data related to the particulate matter, gas pollutants, temperature, and humidity.
Why Air Quality (AQ) Monitoring?
AQ affects how you live and breathe. Like the weather, it can change from day to day or even hour to hour. It is important to have some air pollution monitoring systems to enhance the quality of life. With Air Quality Monitoring device keeping tabs on the shift in air that surrounds us helps in

Controlling as well as preventing certain effects of air pollution

Preventing the change and improves the poor quality of air, ozone depletion, and climate change

