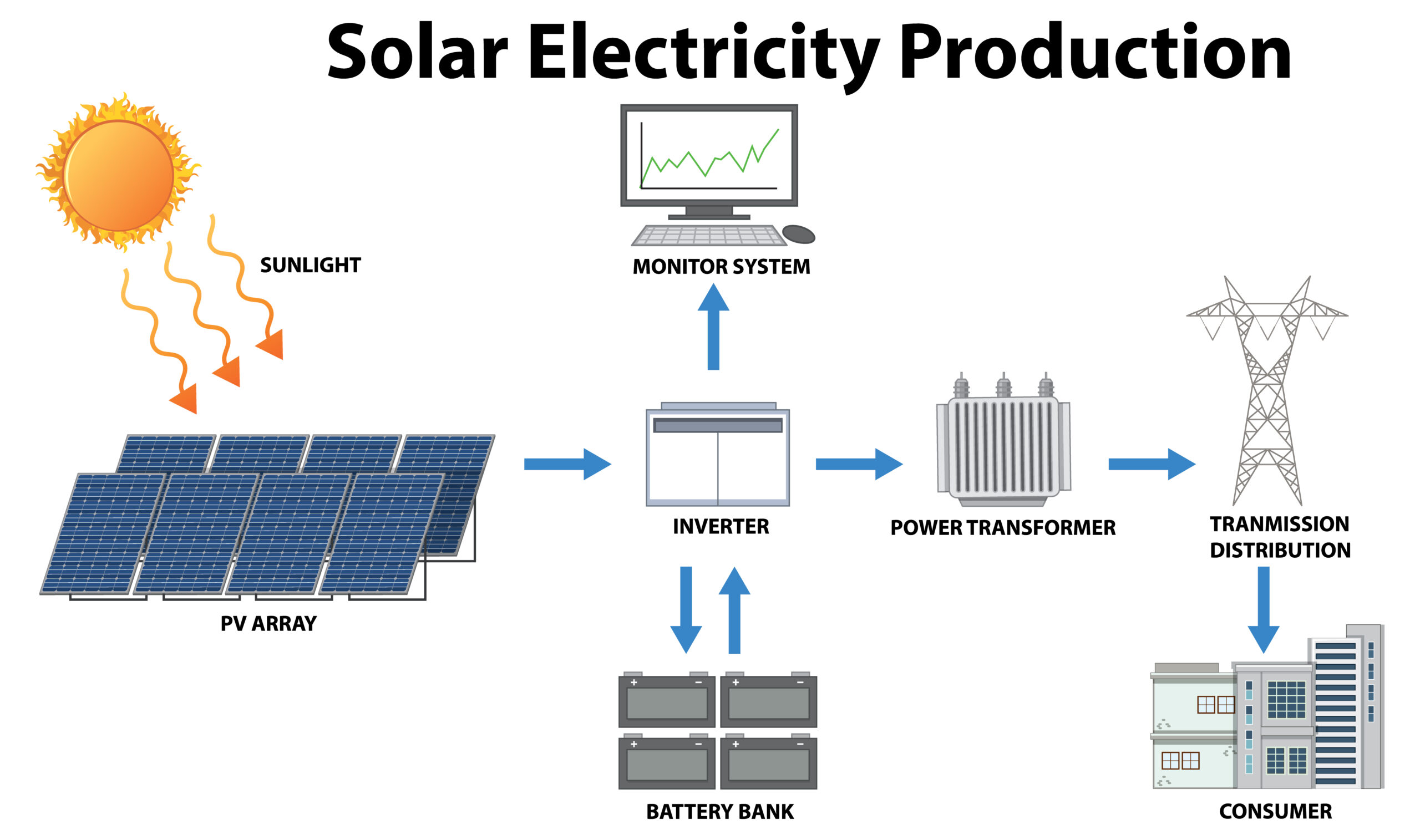
If you’ve ever googled “photovoltaic panels types,” you’ve probably seen terms like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film tossed around. Could you please clarify what they truly mean and help determine which type would be most suitable for you?
Whether you’re planning to install solar panels at home or just curious about how the technology works, this guide will break down the major types of photovoltaic (PV) panels in a way that’s simple, clear, and actionable.
Let’s dive into the world of solar cell technology, panel performance, and what all those blue, black, or even transparent panels are actually doing on rooftops around the world.
What Are Photovoltaic (PV) Panels?
Firstly, photovoltaic panels, also known as PV panels, utilize the photovoltaic effect to transform sunlight into electricity. They’re made of solar cells, and the type of panel depends on how the cells are made and arranged. Each has pros and cons.
The three most common photovoltaic panel types are
Monocrystalline
Polycrystalline
Thin-Film
Let’s explore each in detail.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline panels are the sleek black panels you often see on modern rooftops.
✅ Key Features:
Material: Made from a single, pure silicon crystal
Appearance: Dark black with rounded cell edges
Efficiency: High (18–22%)
Lifespan: 25–30 years
Best for: Homes with limited roof space or those wanting high performance
✅ Pros:
Highest efficiency in real-world conditions
Better performance in heat and low light
Long lifespan and premium build quality
⚠️ Cons:
More expensive than other types
Wastage in production (silicon trimming)
Example: If you live in a city like Mumbai or Delhi with limited roof space, monocrystalline panels will help you generate more electricity in less area.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
These are the blue panels you’ve probably seen in most residential projects over the past decade.
✅ Key Features:
Material: Made from multiple silicon crystals melted together
Appearance: Blue with straight-edged cells
Efficiency: Moderate (15–17%)
Lifespan: 20–25 years
Best for: Budget-conscious homes with ample roof space
✅ Pros:
Lower cost than monocrystalline
Solid performance in sunny climates
Good durability and easy installation
⚠️ Cons:
Slightly lower efficiency
Less aesthetic appeal
Pro Tip: Polycrystalline panels offer a fantastic balance of cost and performance—perfect for larger rooftops where space isn’t a major constraint.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
The outliers in the solar world—these look more like sheets than traditional panels.
✅ Key Features:
Material: Layers of PV material (like CdTe or CIGS) on glass or plastic
Appearance: Uniform, often dark with no visible cells
Efficiency: Low (10–13%)
Lifespan: 15–20 years
Best for: Large industrial spaces, curved surfaces, mobile applications
✅ Pros:
Lightweight and flexible
Sleek design and uniform look
Performs better in shade and high temperatures
⚠️ Cons:
Lower efficiency
Not commonly used for residential rooftops
Shorter lifespan than crystalline panels
Use Case: Ideal for non-traditional surfaces—like curved roofs or temporary solar installations on trailers or tents.
4. Emerging and Specialized photovoltaic panel types
As solar technology evolves, new types of PV panels are entering the market with specialized features.
Bifacial Panels photovoltaic panel types
Capture sunlight from both sides
Ideal for ground-mounted systems with reflective surfaces
Increase energy yield by 10–20%
Perovskite Solar Cells
New tech with high theoretical efficiency and low manufacturing cost
Still under development—expect commercial availability in a few years
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Solar cells embedded in glass, windows, or roofs
Perfect for new buildings where solar can double as construction material
Comparing Photovoltaic Panel Types: At a Glance
Let’s make it even easier to understand. Here’s a quick summary of how these panel types stack up:
Monocrystalline—Best for efficiency and premium builds
Polycrystalline—Best for cost-effectiveness
Thin-Film—Best for design flexibility
Bifacial & BIPV—Great for future-ready solar setups
Which Photovoltaic Panel Types Should You Choose?
This depends on:
Roof space: Limited space = go monocrystalline
Budget: Lower budget = polycrystalline
Design needs: Flexible or BIPV panels suit modern or complex structures
Future plans: Want to stay ahead? Watch out for perovskite or bifacial tech
If you’re getting a solar panel system quote, always ask the provider:
What type of panel are you quoting?
Can I upgrade to a higher-efficiency option?
Is it compatible with hybrid systems or batteries?
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Photovoltaic Technology
Understanding the types of photovoltaic panels helps you make smart decisions for your home or business. Whether you’re focused on aesthetics, budget, or maximum energy yield, there’s a solar panel option that fits your needs.
Remember:
Monocrystalline = Max efficiency
Polycrystalline = Balanced choice
Thin-Film = Niche applications
Emerging tech = Future-ready systems
So the next time someone throws around terms like CIGS, BIPV, or perovskite, you’ll not only know what they mean—you’ll know whether they’re right for your roof.
Read Our Latest Blogs:
FAQs: Photovoltaic Panels Types
Q1: Which type of solar panel is most efficient?
Monocrystalline panels are currently the most efficient, offering up to 22% conversion efficiency.
Q2: Are thin-film panels suitable for home rooftops?
Not usually. They’re better suited for large commercial rooftops or unusual surfaces due to their lower efficiency.
Q3: Can I mix different types of panels in one system?
Not recommended. Different panel types have different voltages and outputs. Mixing them can lower performance and complicate wiring.
Q4: What’s the lifespan of each panel type?
Monocrystalline: 25–30 years
Polycrystalline: 20–25 years
Thin-Film: 15–20 years
Q5: What’s the best type of panel for a north-facing roof?
Consider high-efficiency monocrystalline panels or explore mounting structures that tilt the panels toward the sun.
